Model Context Protocol Server
The Model Context Protocol
Controlling KS Assistant is done by providing MCP clients access to the Assist API of KS Assistant. You can control what devices and entities it can access from the exposed entities page.
Prerequisites
- You need an MCP client
LLM Application such as Claude for Desktop . - Since most clients do not support native remote servers, you need an additional local MCP server remote gateway.
For detailed configuration instructions, refer to the Client configuration section.
Configuration
To add the Model Context Protocol Server service to your KS Assistant instance, use this My button:
If the above My button doesn’t work, you can also perform the following steps manually:
-
Browse to your KS Assistant instance.
-
In the bottom right corner, select the
Add Integration button. -
From the list, select Model Context Protocol Server.
-
Follow the instructions on screen to complete the setup.
Configuration options
The integration provides the following configuration options:
The API to use to expose tools over the Model Context Protocol. It is recommended to use Stateless Assist which is a version of the Assist API where the prompt does not contain any state information. Clients can only control or provide information about entities that are exposed to it.
Architecture overview
This integration can provide similar functionality as other LLM-based conversation agents (for example Anthropic, Google Generative AI, Ollama, Open AI). In those conversation agents, KS Assistant is the client and prepares the available tools and passes them into the LLM with a prompt.
The Model Context Protocol follows a different pattern: An LLM application acts as
a client and can connect to multiple MCP servers to provide context. See the
Model Context Protocol Introduction
The KS Assistant Model Context Protocol Server integration implements the
Server-Sent Events (SSE) transport
Client configuration
The Model Context Protocol specification does not yet define standards for authentication and connecting to remote servers. These are a work in progress and this configuration will likely change in the near future.
Access control
For now, we can use Long-lived access token to control access to the API.
-
Visit your account profile settings, under the Security tab.
.
-
Create a Long-lived access token
-
Copy the access token to use when configuring the MCP client LLM application.
For more information about Authentication in KS Assistant, refer to the Authentication documentation.
Example: Claude for Desktop
See MCP Quickstart: For Claude Desktop Users
Claude for Desktop currently only supports local MCP servers using the stdio
- Download Claude for Desktop
. - Install
mcp-proxyfollowing the instructions in the README. For example, uv tool install git+https://github.com/sparfenyuk/mcp-proxy. - Open the configuration file. Visit Settings… and on the Developer tab, select Edit Config.
which will edit
claude_desktop_config.json. The full file location depends on your operating system (macOS or Windows). - Add a new MCP server to the JSON file. You need to set the
SSE_URLto the URL you use to connect to KS Assistant with the path/mcp_server/sse. You will also need to setAPI_ACCESS_TOKENto the long live access token created above in the access control instructions{ "mcpServers": { "KS Assistant": { "command": "mcp-proxy", "env": { "SSE_URL": "http://localhost:8123/mcp_server/sse", "API_ACCESS_TOKEN": "<your_access_token_here>" } } } } - Restart Claude.
- You will see a connection icon
if things are set up correctly. Clicking the connection icon will show enabled MCP servers such as KS Assistant. - Select the prompt provided by KS Assistant.
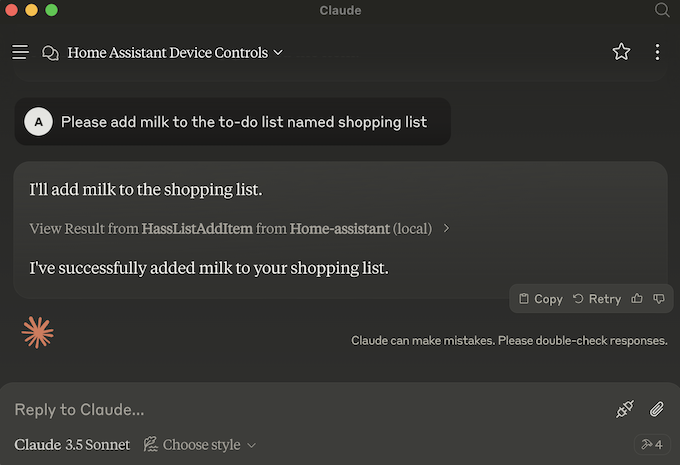
- You can then use Claude to control KS Assistant similar to how you control KS Assistant through the Voice Assistant. Claude wil ask you for permission before calling any tools.
Supported functionality
Tools
MCP Tools
Prompts
The MCP Prompts
It is recommended to use the Stateless Assist API since the prompt does not contain any state information, which will be incorrect after any actions are performed.
Known Limitations
The KS Assistant Model Context Protocol integration currently only supports a subset of MCP features:
| Feature | Supported by KS Assistant |
|---|---|
| Prompts | ✅ |
| Tools | ✅ |
| Resources | ❌ |
| Sampling | ❌ |
| Notifications | ❌ |
KS Assistant does not yet provide built-in tools that can fetch device state.
Troubleshooting
This section has troubleshooting information for Claude for Desktop since it is
the primary client. Also see Debugging in Claude Desktop
LLM client cannot connect to KS Assistant MCP server
Symptom: Failed to start MCP server: Could not start MCP server KS Assistant
When trying to configure a client like Claude for Desktop to talk to KS Assistant, the app shows a message like “Failed to start MCP server: Could not start MCP server KS Assistant”
Description
This means that the local MCP server mcp-proxy could not start.
Resolution
Verify the command line arguments in the claude_desktop_config.json are correct. You may try to run
the command manually to verify that the command can be found.
Symptom: “MCP server KS Assistant disconnected” or “Could not attach to MCP server KS Assistant”
When trying to configure a client like Claude Desktop to talk to KS Assistant, the app shows a message like “MCP server KS Assistant disconnected” or “Could not attach to MCP server KS Assistant”.
Description
This means the MCP server has started, however the MCP server is having trouble communicating with KS Assistant, or the MCP server in KS Assistant is not configured.
Resolution
To understand the root cause, first check debug logs on the client. For example in Claude for Desktop:
- Visit Settings….
- Select Developer.
- Select the
KS AssistantMCP server. - Select Open Logs Folder.
- View
mcp-server-KS Assistant.log. These are known problems and their resolution:-
Client error '404 Not Found' for url 'http://localhost:8123/mcp_server/sse': this means the MCP Server integration is not configured in KS Assistant. -
Client error '401 Unauthorized' for url 'http://localhost:8123/mcp_server/sse': this means that the long live access token is not correct. …
-
Remove integration
This integration can be removed by following these steps:
To remove an integration instance from KS Assistant
- Go to Settings > Devices & services and select the integration card.
- From the list of devices, select the integration instance you want to remove.
- Next to the entry, select the three-dot
menu. Then, select Delete.